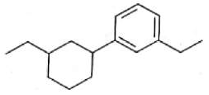
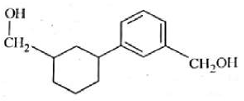
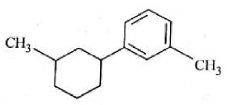
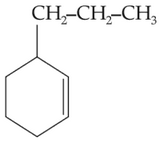
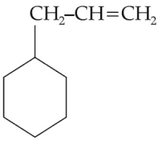
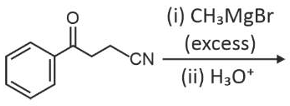
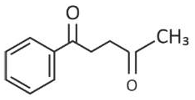
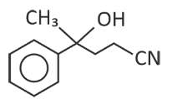
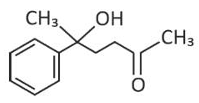
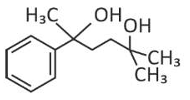
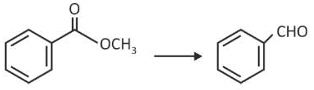
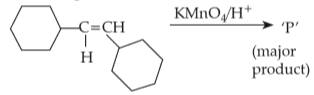
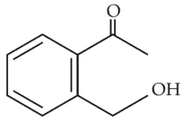
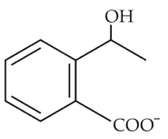
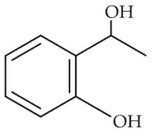
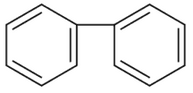
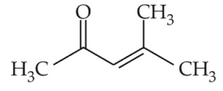
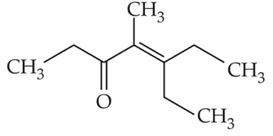
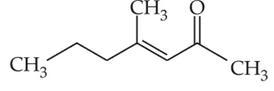
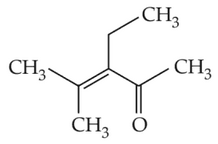
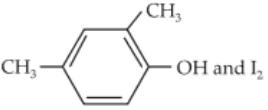
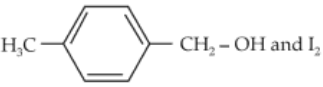
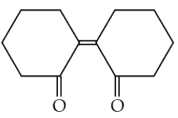
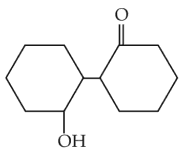
Home >> Topics >> Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Unattempted Questions
Questions Available: 22
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2022
Topic: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
11.
Given below are two statements :
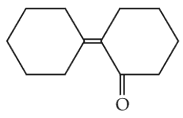
Statement I : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons ofcomparable molecular masses because of weakmolecular association in aldehydes and ketones dueto dipole - dipole interactions.
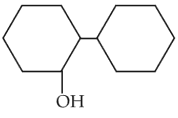
Statement II : The boiling points of aldehydesand ketones are lower than the alcohols of similarmolecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding.
In the light of the above statements, choose themost appropriate answer from the given below:
Statement I : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons ofcomparable molecular masses because of weakmolecular association in aldehydes and ketones dueto dipole - dipole interactions.
Statement II : The boiling points of aldehydesand ketones are lower than the alcohols of similarmolecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding.
In the light of the above statements, choose themost appropriate answer from the given below: