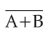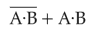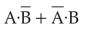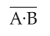Home >> NEET - 2018
Welcome and Shine in NEET with Shine NEET SmartPrep!.
Please register for a Free trial. You would be able to try a sub set of these questions in your free trial. We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Register
Please register for a Free trial. You would be able to try a sub set of these questions in your free trial. We recommend you explore the full system and go for a one time subscription if you are satisfied.
Try it out and feel the difference!!
Register
Your Full Test Performance Summary
Questions Available: 180
Questions Attempted: 0
Number of Attempts: 0
Correct Attempts: 0
Total Time Spent: 00:00
Avg Time Per Question: 00:00
1.
An object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. If the object is displaced through a distance of 20 cm towards the mirror, the displacement of the image will be
2.
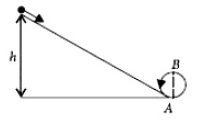
A body initially at rest and sliding along a frictionless track from a height h (as shown in the figure) just completes a vertical circle of diameter AB = D.The height h is equal to

3.
Unpolarised light is incident from
air on a plane surface of a material of refractive index ‘μ’. At a particular angle of incidence ‘i ’, it is found that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other. Which of the following options is correct for this situation?
4.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclination θ as shown in the figure.
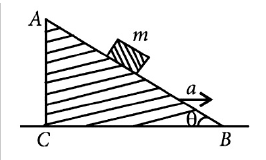
The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is

The wedge is given an acceleration a towards the right. The relation between a and θ for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is
5.
A moving block having mass m, collides with another stationary block having mass 4m. The lighter block comes to rest after collision. When the initial velocity of the lighter block is v, then the value of coefficient of restitution (e) will be
6.
The refractive index of the material of a prism is 2 and the angle of the prism is \(30^\circ\). One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is made a mirror inwards, by silver coating. A beam of monochromatic light entering the prism from the other face will retrace its path (after reflection from the silvered surface) if its
angle of incidence on the prism is
7.
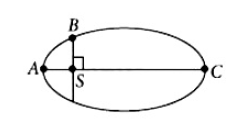
The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) are \(K_A\), \(K_B\) and \(K_C\), respectively. \(AC\) is the major axis and \(SB\) is perpendicular to \(AC\) at the position of the Sun \(S\) as shown in the figure. Then

8.
If the mass of the Sun were ten times smaller and the universal gravitational constant were ten times larger in magnitude, which of the following is not correct?
9.
In Young’s double slit experiment, the separation "d" between the slits is 2 mm, the wavelength \(\lambda\) of the light used is 5896 Å and distance "D" between the screen and slits is 100 cm. It is found that the angular width of the fringes is 0.20°. To increase the fringe angular width to 0.21° (with same l and D) the separation between the slits needs to be changed to
10.
A student measured the diameter of a small steel ball using a screw gauge of least count 0.001 cm. The main scale reading is 5 mm and zero of circular scale division coincides with 25 divisions above the reference level. If screw gauge has a zero error of -0.004 cm, the correct diameter of the ball is
11.
An astronomical refracting telescope will have large angular magnification and high angularresolution, when it has an objective lens of
12.
A sample of 0.1 g of water at 100°C and normal pressure (\(1.013 \times 10^5 Nm^{-2}\) ) requires 54 cal of heat energy to convert to steam at 100°C. If the volume of the steam produced is 167.1 cc, the change in internal energy of the sample,
13.
A solid sphere is in rolling motion. In rolling motion a body possesses translational kinetic energy (\(K_t\)) as well as rotational kinetic energy (\(K_r\)) simultaneously. The ratio \(K_t\,:\,\)(\( K_t\, +\, K_ r\)) for the sphere is
14.
A solid sphere is rotating freely about its symmetry axis in free space.The radius of the sphere is increased keeping its mass same. Which ofthe following physical quantities would remain constant for the sphere?
15.
Three objects, A (a solid sphere), B (a thin circular disk) and C (a circular ring), each have the same mass M and radius R. They all spin with the same angular speed ω about their own symmetry axes. The amounts of work (W) required to bring them to rest, would satisfy the relation
16.
The volume (V) of a monoatomic gas varies with its temperature (T), as shown in the graph. The ratio of work done by the gas, to the heat absorbed by it, when it undergoes a change from state A to state B, is
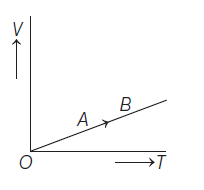

17.
The moment of the force, \(\vec{F} = 4\hat{i} + 5\hat{j} − 6\hat{k}\) at (2, 0, −3), about the point (2, −2, −2), is given by
18.
At what temperature will the rms speed of oxygen molecules become just sufficient for escaping from the Earth’s atmosphere?
(Given: mass of oxygen molecule,\(m = 2.76 × 10^−{26}\, kg\) ,Boltzmann’s constant\(k_B = 1.38 10^{-23} J K^{ −1}\))
(Given: mass of oxygen molecule,\(m = 2.76 × 10^−{26}\, kg\) ,Boltzmann’s constant\(k_B = 1.38 10^{-23} J K^{ −1}\))
19.
An electron of mass m with an initial velocity \(\vec{v}\,=v_0\hat{i} \left( v_0\,>\,0 \right)\) enters an electric field \(\vec{E}\,=\,-\vec{E}_0 \hat{i} \left ( E_0 \,=\, constant\, >\, 0 \right )\) at t = 0. If \(λ_0\) is its de-Broglie wavelength initially, then its de-Broglie wavelength at time t is
20.
When the light of frequency \(2v_0\)
(where \(v_0\)
is threshold frequency), is
incident on a metal plate, the maximum velocity of electrons emitted is
\(v_1\)
. When the frequency of the incident radiation is increased to \(5v_0\)
, the
maximum velocity of electrons emitted from the same plate is \(v_2\)
. The
ratio of \(v_1\)
to \(v_2\)
is
21.
A small sphere of radius \('r'\) falls from rest in a viscous liquid. As a result, heat is produced due to viscous force. The rate of production of heat when the sphere attains its terminal velocity, is proportional to
22.
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume.The first wire has cross-sectional area A and the second wire has cross-sectional area 3A. If the length of the first wire is increased by \(\Delta l \) on applying a force \(F\) , how much force is needed to stretch the second wire by the same amount?
23.
The power radiated by a black body is \(P\) and it radiates maximum energy at wavelength, \(\lambda_0\). If the temperature of the black body is now changed so that it radiates maximum energy at wavelength \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{4} \lambda_0\), the power radiated by it becomes \(n\,p\). The value of n is
24.
In the combination of the following gates the output Y can be written in terms of inputs A and B as
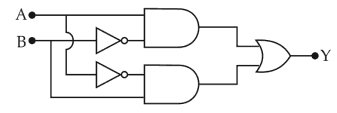

25.
In the circuit shown in the figure,
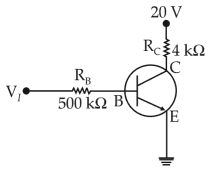
the input voltage \(V_i\) is 20 V , \(V_{BE}\) = 0 and \(V_{CE}\) = 0. The values of \(I_B\), \(I_C\)and β are given by

the input voltage \(V_i\) is 20 V , \(V_{BE}\) = 0 and \(V_{CE}\) = 0. The values of \(I_B\), \(I_C\)and β are given by
26.
In a p − n junction diode, change in temperature due to heating
27.
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ , when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance
28.
An inductor 20 mH , a capacitor 100 μF and a resistor 50 Ω are connected in series across a source of emf,
V = 10 sin 314 t. The power loss in the circuit is
V = 10 sin 314 t. The power loss in the circuit is
29.
A pendulum is hung from the roof of a sufficiently high building and is moving freely to and fro like a simple harmonic oscillator. The acceleration of the bob of the pendulum is \(20ms^{−2}\) at a distance of 5m from the mean position. The time period of oscillation is
30.
The ratio of kinetic energy to the total energy of an electron in a Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom, is
31.
For a radioactive material, half-life is 10 minutes. If initially there are 600 number of nuclei, the time taken (in minutes) for the disintegration of 450 nuclei is
32.
A tuning fork is used to produce resonance in a glass tube. The length of the air column in this tube can be adjusted by a variable piston. At room temperature of \(27^\circ C\) two successive resonances are produced at \(20\,cm\) and \(73\,cm\) of column length. If the frequency of the tuning fork is \(320\,Hz\), the velocity of sound in air at \(27^\circ C\) is
33.
The fundamental frequency in an open organ pipe is equal to the third harmonic of a closed organ pipe. If the length of the closed organ pipe is \(20\,cm\), the length of the open organ pipe is
34.
An electron falls from rest through a vertical distance h in a uniform and vertically upward directed electric field E. The direction of electric field is now reversed, keeping its magnitude the same. A proton is allowed to fall from rest in it through the same vertical distance h. The time of fall of the electron, in comparison to the time of fall of the proton is
35.
The electrostatic force between the metal plates of an isolated parallel plate capacitor C having a charge Q and area A, is
36.
A toy car with charge q moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field \(\vec{E}\). Due to the force q \(\vec{E}\), its velocity increases from 0 to 6 ms−1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively
37.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
38.
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from
39.
The efficiency of an ideal heat engine working between the freezing point and boiling point of water, is
40.
A set of n equal resistors, of value R each, are connected in series to abattery of emf E and internal resistance R. The current drawn is I .Now, the n resistors are connected in parallel to the same battery. Then the current drawn from battery becomes 10 I . The value of n is
41.
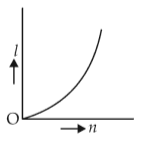
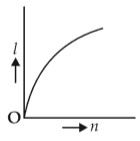
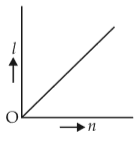
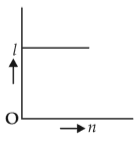
A battery consists of a variable number n of identical cells (havinginternal resistance r each ) which are connected in series. The terminals of the battery are short-circuited and the current I is measured. Whichof the graphs shows the correct relationship between I and n?
42.
A carbon resistor of (47 ± 4.7) kΩ is to be marked with rings of different colours for its identification. The colour code sequence will be
43.
An em wave is propagating in a medium with a velocity \(\vec{v}=v\,\hat{i}\). The instantaneous oscillating electric field of this em wave is along +y axis. Then the direction of oscillating magnetic field of the em wave will be along
44.
A metallic rod of mass per unit length 0.5 kgm−1 is lying horizontally on a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle of \(30^\circ\) with the horizontal. The rod is not allowed to slide down by flowing a current through it when a magnetic field of induction 0.25 T is acting on it in the vertical direction. The current flowing in the rod to keep it stationary is
45.
Current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is 5 div/mA and its voltage sensitivity (angular deflection per unit voltage applied) is 20 div/V. The resistance of the galvanometer is
46.
Which oxide of nitrogen is not a common pollutant introduced into the atmosphere both due to natural and human activity ?
47.
Given van der Waals constant for NH3, H2, O2 and CO2 are respectively 4.17, 0.244, 1.36 and 3.59, which one of the following gases is most easily liquefied ?
48.
In the structure of ClF3, the number of lone pair of electrons on central atom ‘Cl’ is
49.
The correct order of atomic radii in group 13 elements is
50.
Match the metal ions given in Column I with the spin magnetic moments of the ions given in Column II and assign the correct code


51.
The geometry and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4] are
52.
Which of the following molecules represents the order of hybridization sp2, sp2, sp, sp from left to right atoms ?
53.
Among CaH2 , BeH2, BaH2 , the order of ionic character is
54.
Consider the change in oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below
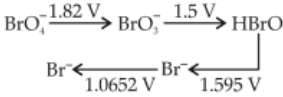
Then the species undergoing dispro-portionation is
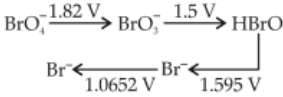
Then the species undergoing dispro-portionation is
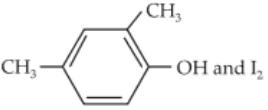
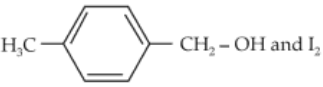
55.
In which case is number of molecules of water maximum ?
56.
The compound A on treatment with Na gives B, and with PCl5 gives C. B and C react together to give diethyl ether. A, B and C are in the order
57.
Hydrocarbon (A) reacts with bromine by substitution to form an alkyl bromide which by Wurtz reaction is converted to gaseous hydrocarbon containing less than four carbon atoms. (A) is
58.
The compound C7H8 undergoes the following reactions:
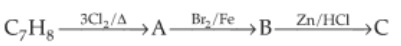
The product 'C' is
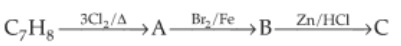
The product 'C' is
59.
A mixture of 2.3 g formic acid and 4.5 g oxalic acid is treated with conc. H2SO4. The evolved gaseous mixture is passed through KOH pellets. Weight (in g) of the remaining product at STP will be
60.
The difference between amylose and amylopectin is
61.
Which of the following oxides is most acidic in nature ?
62.
Nitration of aniline in strong acidic medium also gives m-nitroaniline because
63.
Regarding cross-linked or network polymers, which of the following statements is incorrect ?
64.
Following solutions were prepared by mixing different volumes of NaOH and HCl of different concentrations:
A. \( \text{60 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{40 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
B. \( \text{55 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{45 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
C. A. \( \text{75 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{5}}\)HCl + \( \text{25 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{5}}\)NaOH
D. \( \text{100 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{100 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
pH of which one of them will be equal to 1 ?
A. \( \text{60 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{40 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
B. \( \text{55 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{45 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
C. A. \( \text{75 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{5}}\)HCl + \( \text{25 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{5}}\)NaOH
D. \( \text{100 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)HCl + \( \text{100 mL} \frac{\text{M}}{\text{10}}\)NaOH
pH of which one of them will be equal to 1 ?
65.
On which of the following properties does the coagulating power of an ion depend ?
66.
The solubility of BaSO4 in water is 2.42 × 10–3gL–1 at 298 K. The value of its solubility product (Ksp) will be
(Given molar mass of BaSO4 = 233 g mol–1)
(Given molar mass of BaSO4 = 233 g mol–1)
67.
Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is 1s2 2s2 2p3, the simplest formula for this compound is
68.
Iron exhibits bcc structure at room temperature. Above 900°C, it transforms to fcc structure. The ratio of density of iron at room temperature to that at 900°C (assuming molar mass and atomic radii of iron remains constant with temperature) is
69.
Which one is a wrong statement ?
70.
Consider the following species:
CN+, CN–, NO and CN
Which one of these will have the highest bond order ?
CN+, CN–, NO and CN
Which one of these will have the highest bond order ?
71.
Which of the following statements is not true for halogens ?
72.
Which one of the following elements is unable to form \(\text{MF}_^{3-} ion ?
73.
Considering Ellingham diagram, which of the following metals can be used to reduce alumina ?
74.
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is
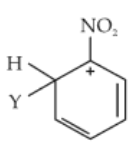
75.
In the reaction, the electrophile involved is
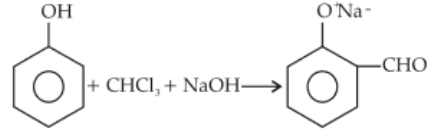
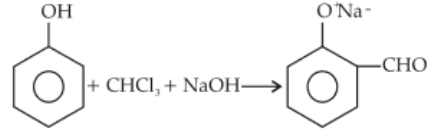
76.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
77.
Compound A, C8H10O, is found to react with NaOI (produced by reacting Y with NaOH) and yields a yellow precipitate with characteristic smell.
A and Y are respectively :
A and Y are respectively :
78.
Iron carbonyl, Fe(CO) 5 is
79.
Which one of the following ions exhibits d-d transition and paramagnetism as well ?
80.
The type of isomerism shown by the complex [CoCl2(en)2] is
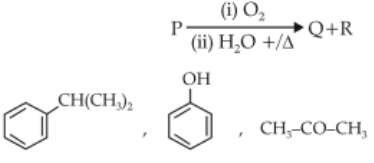
81.
Identify the major products P, Q and R in the following sequence of reactions
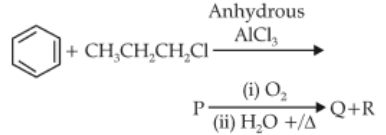

82.
Which of the following compounds can form a zwitter ion ?
83.
For the redox reaction
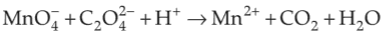
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced equation are
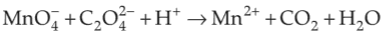
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced equation are
84.
The correction factor ‘a’ to the ideal gas equation corresponds to
85.
Which one of the following conditions will favour maximum formation of the product in the reaction,
A2(g) + B2(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \) X2(g) \(\Delta_r\)H = -XkJ?
A2(g) + B2(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \) X2(g) \(\Delta_r\)H = -XkJ?
86.
The bond disssociation energies of X2, Y2 and XY are in the ratio 1 : 0.5 : 1. \(\Delta\)H for the formation of XY is -200 KJ mol-. The bond dissociation energy of X2 will be
87.
When initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of a zero order reaction
88.
Which of the following carbocations is expected to be most stable ?
89.
Which of the following is correct with respect to -1 effect of yje substituents? (R = alkyl)
90.
The correct difference between first and second order reactions is that
91.
Select the correct match
92.
Which of the following has proved helpful in preserving pollen as fossils?
93.
Stomatal movement is not affected by
94.
Which of the following is true for nucleolus?
95.
After karyogamy followed by meiosis, spores are produced exogenously in
96.
Which one of the following plants shows a very close relationship with a species of moth, where none of the two can complete its life cycle without the other?
97.
Pollen grains can be stored for several years in liquid nitrogen having a temperature of
98.
Which of the following elements is responsible for maintaining turgor in cells ?
99.
Plants having little or no secondary growth are
100.
Many ribosomes may associate with a single mRNA to form multiple copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. Such strings of ribosomes are termed as
101.
Which one of the following population interactions is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics ?
102.
A woman has an X-linked condition on one of her X chromosomes. This chromosome can be inherited by
103.
According to Hugo de Vries, the mechanism of evolution is
104.
All of the following are part of an operon except
105.
Niche is
106.
Which of the following is a secondary pollutant ?
107.
In stratosphere, which of the following elements acts as a catalyst in degradation of ozone and release of molecular oxygen ?
108.
World Ozone Day is celebrated on
109.
What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data ?
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g Primary producer : 10 g
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g Primary producer : 10 g
110.
Natality refers to
111.
Offsets are produced by
112.
The experimental proof for semi-conservative replication of DNA was first shown in a
113.
Which of the following pairs is wrongly matched?
114.
Which of the following flowers only once in its life-time?
115.
Select the correct statement.
116.
The Golgi complex participates in
117.
The stage during which separation of the paired homologous chromosomes begins is
118.
Stomata in grass leaf are
119.
Which of the following is not a product of light reaction of photosynthesis ?
120.
Which among the following is not a prokaryote?
121.
The two functional groups characteristic of sugars are
122.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
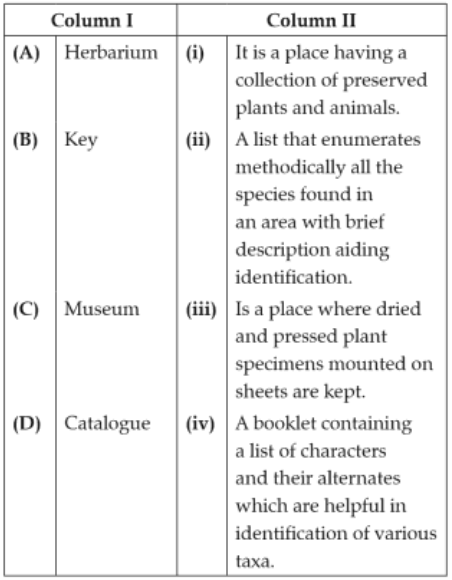

123.
Which one is wrongly matched?
124.
Winged pollen grains are present in
125.
Which of the following is commonly used as a vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human lymphocytes?
126.
A ‘new’ variety of rice was patented by a foreign company, though such varieties have been present in India for a long time. This is related to
127.
Use of bioresources by multinational companies and organisations without authorisation from the concerned country and its people is called
128.
Select the correct match:
129.
The correct order of steps in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is
130.
In India, the organisation responsible for assessing the safety of introducing genetically modified organisms for public use is
131.
What is the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
132.
In which of the following forms is iron absorbed by plants?
133.
Double fertilisation is
134.
Oxygen is not produced during photosynthesis by
135.
Pneumatophores occur in
136.
Select the wrong statement.
137.
Secondary xylem and phloem in dicot stem are produced by
138.
Sweet potato is a modified
139.
Which of the following statements is correct?
140.
Casparian strips occur in
141.
Nissl bodies are mainly composed of
142.
Which of these statements is incorrect?
143.
Which of the following terms describe human dentition?
144.
Which of the following events does not occur in rough endoplasmic reticulum?
145.
Select the incorrect match
146.
Which of the following is an amino acid derived hormone?
147.
Which of the following structures or regions is incorrectly paired with its functions?
148.
Which of the following hormones can play a significant role in osteoporosis?
149.
The transparent lens in the human eye is held in its place by
150.
In a growing population of a country,
151.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below :


152.
Which part of poppy plant is used to obtain the drug “Smack”?
153.
All of the following are included in ‘ex-situ conservation’ except
154.
Which of the following gastric cells indirectly help in erythropoiesis?
155.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
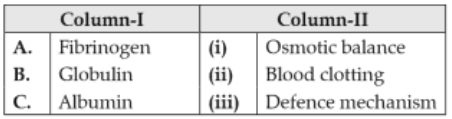

156.
Calcium is important in skeletal muscle contraction because it
157.
Which of the following is an occupational respiratory disorder?
158.
AGGTATCGCAT is a sequence from the coding strand of a gene. What will be the corresponding sequence of the transcribed mRNA?
159.
Match the items in column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
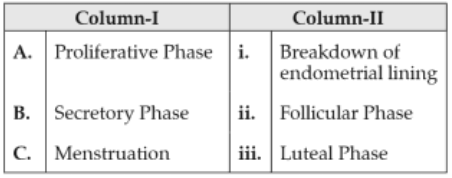

160.
Which of the following options correctly represents the lung conditions in asthma and emphysema, respectively ?
161.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below :
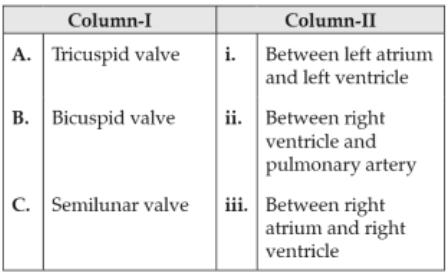

162.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below :
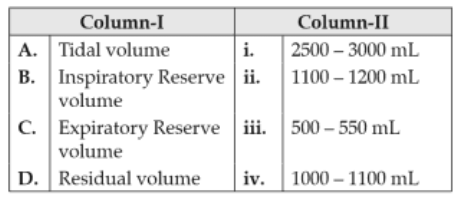

163.
Hormones secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy are
164.
The contraceptive ‘SAHELI’
165.
The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is
166.
The amnion of mammalian embryo is derived from
167.
Which of the following animals does not undergo metamorphosis?
168.
Which one of these animals is not a homeotherm?
169.
Which of the following features is used to identify a male cockroach from a female cockroach?
170.
Which of the following organisms are known as chief producers in the oceans ?
171.
Ciliates differ from all other protozoans in
172.
Identify the vertebrate group of animals characterized by crop and gizzard in its digestive system
173.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
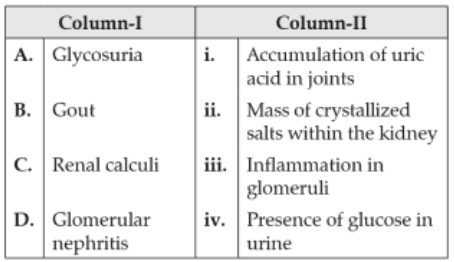

174.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below:
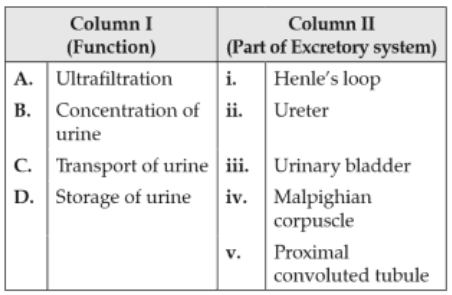

175.
Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option
176.
Conversion of milk to curd improves its nutritional value by increasing the amount of
177.
Which of the following characteristics represent Inheritance of blood groups' in humans?
A. Dominance
B. Co - dominance
C. Multiple allele
D. Incomplete dominance
E. Polygenic inheritance
A. Dominance
B. Co - dominance
C. Multiple allele
D. Incomplete dominance
E. Polygenic inheritance
178.
Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease?
179.
The similarity of bone structure in the forelimbs of many vertebrates is an example of
180.
In which disease does mosquito transmitted pathogen cause chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels ?