Home >> My Performance >> My Topic Test Performance >> My Question Performance
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests !
Questions Available: 21
Questions Attempted: 10
Number of Attempts: 15
Correct Attempts: 8
Total Time Spent: 00:30
Avg Time Per Question: 00:02
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests
In the given figure, which component has thin outer walls and highly thickened inner walls?
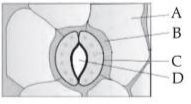
(1). A
(2). B
(3). C
(4). D

(1). A
(2). B
(3). C
(4). D
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Plants having little or no secondary growth are
(1). cycads.
(2). conifers.
(3). deciduous angiosperms.
(4). grasses.
(1). cycads.
(2). conifers.
(3). deciduous angiosperms.
(4). grasses.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Find the statement that is NOT correct with regard to the structure of monocot stem.
(1). Phloem parenchyma is absent.
(2). Hypodermis is parenchymatous.
(3). Vascular bundles are scattered.
(4). Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
(1). Phloem parenchyma is absent.
(2). Hypodermis is parenchymatous.
(3). Vascular bundles are scattered.
(4). Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Bulliform cells are responsible for-
(1). Increased photosynthesis in monocots
(2). Providing large spaces for storage of sugars
(3). Inward curling of leaves in monocots
(4). Protecting the plant from salt stress
(1). Increased photosynthesis in monocots
(2). Providing large spaces for storage of sugars
(3). Inward curling of leaves in monocots
(4). Protecting the plant from salt stress
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Formation of interfascicular cambium from fully developed parenchyma cells is an example for
(1). Dedifferentiation
(2). Maturation
(3). Differentiation
(4). Redifferentiation
(1). Dedifferentiation
(2). Maturation
(3). Differentiation
(4). Redifferentiation
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Given below are two statements: One is labelled
as Assertion A and the other is labelled as
Reason R:
Assertion A : Late wood has fewer xylary elements with narrow vessels.
Reason R: Cambium is less active in winters.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(1). Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(2). A is true but R is false.
(3). A is false but R is true.
(4). Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Assertion A : Late wood has fewer xylary elements with narrow vessels.
Reason R: Cambium is less active in winters.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(1). Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(2). A is true but R is false.
(3). A is false but R is true.
(4). Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Cellulose does not form blue colour with lodine
because:
(1). It is a helical molecule.
(2). It does not contain complex helices and hence can not hold iodine molecules.
(3). It breakes down when iodine reacts with it.
(4). It is a disaccharide.
(1). It is a helical molecule.
(2). It does not contain complex helices and hence can not hold iodine molecules.
(3). It breakes down when iodine reacts with it.
(4). It is a disaccharide.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Match List -I with List -II
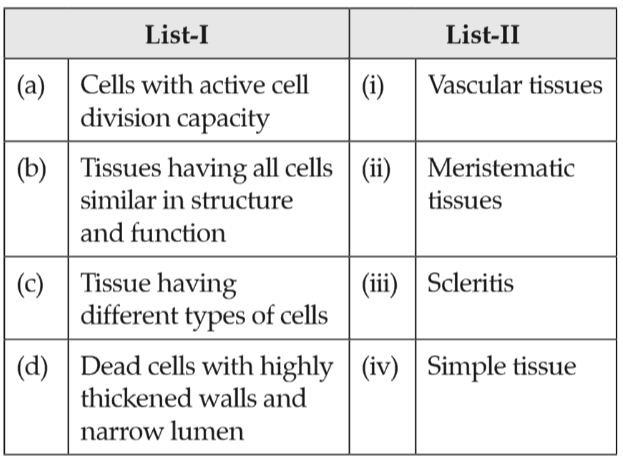
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(1). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
(2). (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(3). (a) - (i), (b) - (ii), (c) - (iii), (d)- (iv)
(4). (a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) -(iv), (d) - (i)

Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(1). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
(2). (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(3). (a) - (i), (b) - (ii), (c) - (iii), (d)- (iv)
(4). (a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) -(iv), (d) - (i)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Match List - I with List - II
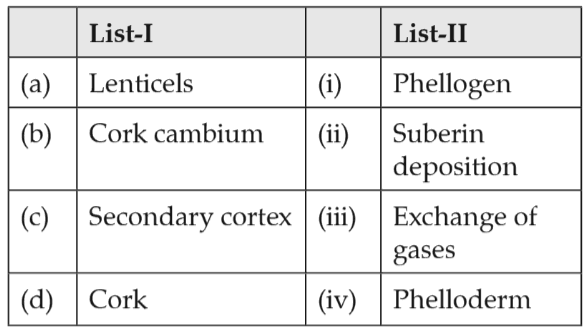
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(1). (a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
(2). (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
(3). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(4). (a) - (iv), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)

Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(1). (a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
(2). (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
(3). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(4). (a) - (iv), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Select the correct pair.
(1). Large colorless empty cells in the epidermis of grass leaves - Subsidiary Cells
(2). In dicot leaves, vascular bundles are surrounded by large thick-walled cells - Conjunctive Tissue
(3). Cells of medullary rays that form part of cambial ring - Interfascicular cambium
(4). Loose parenchyma cells rupturing the epidermis and forming a lens shaped opening in the bark - Spongy Parenchyma
(1). Large colorless empty cells in the epidermis of grass leaves - Subsidiary Cells
(2). In dicot leaves, vascular bundles are surrounded by large thick-walled cells - Conjunctive Tissue
(3). Cells of medullary rays that form part of cambial ring - Interfascicular cambium
(4). Loose parenchyma cells rupturing the epidermis and forming a lens shaped opening in the bark - Spongy Parenchyma
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
ldentify the incorrect statement.
(1). Sapwood is involved in conduction of water and minerals from root to leaf.
(2). Sapwood is the innermost secondary xylem and is lighter in colour.
(3). Due to deposition of tannins, resins, oils etc., heart wood is dark in colour.
(4). Heart wood does not conduct water but gives mechanical support.
(1). Sapwood is involved in conduction of water and minerals from root to leaf.
(2). Sapwood is the innermost secondary xylem and is lighter in colour.
(3). Due to deposition of tannins, resins, oils etc., heart wood is dark in colour.
(4). Heart wood does not conduct water but gives mechanical support.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The transverse section of a plant shows following
anatomical features:
(a) Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(b) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(c) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(d) Phloem parenchyma absent.
ldentify the category of plant and its part:
(1). Monocotyledonous root
(2). Dicotyledonous stem
(3). Dicotyledonous root
(4). Monocotyledonous stem
(a) Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(b) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(c) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(d) Phloem parenchyma absent.
ldentify the category of plant and its part:
(1). Monocotyledonous root
(2). Dicotyledonous stem
(3). Dicotyledonous root
(4). Monocotyledonous stem
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Phloem in gymnosperms lacks
(1). sieve tubes only.
(2). companion cells only.
(3). both sieve tubes and companion cells.
(4). albuminous cells and sieve cells.
(1). sieve tubes only.
(2). companion cells only.
(3). both sieve tubes and companion cells.
(4). albuminous cells and sieve cells.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Which of the statements given below is not true about formation of annual rings in trees ?
(1). Differential activity of cambium causes light and dark bands of tissue-early and late wood respectively.
(2). Activity of cambium depends upon variation in climate.
(3). Annual rings are not prominent in trees of temperate region.
(4). Annual ring is a combination of spring wood and autumn wood produced in a year.
(1). Differential activity of cambium causes light and dark bands of tissue-early and late wood respectively.
(2). Activity of cambium depends upon variation in climate.
(3). Annual rings are not prominent in trees of temperate region.
(4). Annual ring is a combination of spring wood and autumn wood produced in a year.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Stomata in grass leaf are
(1). barrel shaped.
(2). rectangular.
(3). kidney shaped.
(4). dumb-bell shaped.
(1). barrel shaped.
(2). rectangular.
(3). kidney shaped.
(4). dumb-bell shaped.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Secondary xylem and phloem in dicot stem are produced by
(1). axillary meristems.
(2). phellogen.
(3). vascular cambium.
(4). apical meristems.
(1). axillary meristems.
(2). phellogen.
(3). vascular cambium.
(4). apical meristems.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Casparian strips occur in
(1). endodermis.
(2). cortex.
(3). pericycle.
(4). epidermis.
(1). endodermis.
(2). cortex.
(3). pericycle.
(4). epidermis.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Which of the following is made up of dead cells ?
(1). Phloem
(2). Xylem parenchyma
(3). Collenchyma
(4). Phellem
(1). Phloem
(2). Xylem parenchyma
(3). Collenchyma
(4). Phellem
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Identify the wrong statement in context of heartwood
(1). It comprises dead elements with highly lignified walls.
(2). Organic compounds are deposited in it.
(3). It is highly durable.
(4). It conducts water and minerals efficiently.
(1). It comprises dead elements with highly lignified walls.
(2). Organic compounds are deposited in it.
(3). It is highly durable.
(4). It conducts water and minerals efficiently.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Root hairs develop from the region of
(1). Meristematic activity
(2). Maturation
(3). Elongation
(4). Root cap
(1). Meristematic activity
(2). Maturation
(3). Elongation
(4). Root cap
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Specialised epidermal cells surrounding the guard cells are called
(1). subsidiary cells
(2). bulliform cells
(3). lenticels
(4). complementary cells
(1). subsidiary cells
(2). bulliform cells
(3). lenticels
(4). complementary cells
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
