Home >> My Performance >> My Topic Test Performance >> My Question Performance
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests !
Questions Available: 27
Questions Attempted: 10
Number of Attempts: 15
Correct Attempts: 8
Total Time Spent: 00:30
Avg Time Per Question: 00:02
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests
The moment of inertia of a thin rod about an axis passing through its mid point and perpendicular to the rod is 2400 gcm2. The length of the 400 g rod is nearly:
(1). 8.5
(2). 17.5
(3). 20.7
(4). 72.0
(1). 8.5
(2). 17.5
(3). 20.7
(4). 72.0
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The angular acceleration of a body, moving along the circumference of a circle, is
(1). Along the radius towards the centre
(2). Along the tangent to its position
(3). Along the axis of rotation
(4). Along the radius, away from centre
(1). Along the radius towards the centre
(2). Along the tangent to its position
(3). Along the axis of rotation
(4). Along the radius, away from centre
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
From a circular ring of mass ' M ' and radius ' R ' an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining partof the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ' K ' times ′M R2'. Then the value of ' K ' is
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{4}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{8}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{4}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{8}\)
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{4}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{8}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{4}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{8}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
From a disc of radius R and mass M, a circular hole of diameter R, whose rim passes through the centre is cut. What is the moment of inertia of the remaining part of the disc about a perpendicular axis, passing through the centre?
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{11\, MR^2}{32}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{9\, MR^2}{32}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{15 MR^2}{32}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{13 MR^2}{32}\)
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{11\, MR^2}{32}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{9\, MR^2}{32}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{15 MR^2}{32}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{13 MR^2}{32}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The sun rotates around its centre once in 27 days. What will be the period of revolution if the Sun were to expand to twice its present radius without any external influence? Assume the Sun to be a sphere of uniform density.
(1). 108 days
(2). 100 days
(3). 105 days
(4). 115 days
(1). 108 days
(2). 100 days
(3). 105 days
(4). 115 days
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A uniform rod of mass 20 kg and length 5 m leans against a smooth vertical wall making an angle of 60° with it. The other end rests on a rough horizontal floor. The friction force that the floor exerts on the rod is
(take \( g\, =\, 10 \text{m/s}^2\))
(1). \(200\, \sqrt{3}\, \text{N}\)
(2). \(100\, \sqrt{N}\)
(3). \(100 \, \sqrt{3}\, \text{N}\)
(4). \(200\, \text{N}\)
(1). \(200\, \sqrt{3}\, \text{N}\)
(2). \(100\, \sqrt{N}\)
(3). \(100 \, \sqrt{3}\, \text{N}\)
(4). \(200\, \text{N}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A sphere of radius R is cut from a larger solid sphere of radius 2R as shown in the figure. The ratio of the moment of inertia of the smaller sphere to that of the rest part of the sphere about the Y-axis is :
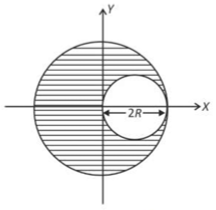
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{64}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{8}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{40}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{57}\)

(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{64}\)
(2). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{8}\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{40}\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{7}{57}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A wheel of a bullock cart is rolling on a level road as shown in the figure below. If its linear speed is ν in the direction shown, which one of the following options is correct (P and Q are any highest and lowest points on the wheel, respectively)?
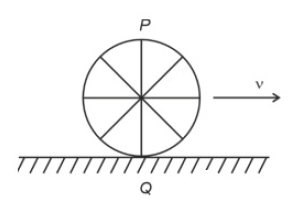
(1). Point P moves slower than point Q
(2). Point P moves faster than point Q
(3). Both the points P and Q move with equal speed
(4). Point P has zero speed

(1). Point P moves slower than point Q
(2). Point P moves faster than point Q
(3). Both the points P and Q move with equal speed
(4). Point P has zero speed
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The ratio of radius of gyration of a solid sphere of mass M and radius R about its own axis to the radius of gyration of the thin hollow sphere of same mass and radius about its axis is
(1). 5:3
(2). 2:5
(3). 5:2
(4). None of the above
(1). 5:3
(2). 2:5
(3). 5:2
(4). None of the above
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A shell of mass m is at rest initially. It explodes into three fragments having mass in the ratio 2 : 2 : 1. If the fragments having equal mass flyoff along mutually perpendicular directions with speed v, the speed of the third (lighter) fragment is
(1). v
(2). \(\sqrt{2}\) v
(3). 2\(\sqrt{2}\) v
(4). 3\(\sqrt{2}\) v
(1). v
(2). \(\sqrt{2}\) v
(3). 2\(\sqrt{2}\) v
(4). 3\(\sqrt{2}\) v
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The angular speed of a fly wheel moving with uniform angular acceleration changes from 1200 rpm to 3120 rpm in 16 seconds. The angular acceleration in rad ∕ s2 is
(1). \(2\pi\)
(2). \(4\pi\)
(3). \(12\pi\)
(4). \(104\pi\)
(1). \(2\pi\)
(2). \(4\pi\)
(3). \(12\pi\)
(4). \(104\pi\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Two objects of mass 10 kg and 20 kg respectively are connected to the two ends of a rigid rod of length 10 m with negligible mass. The distance of the center of mass of the system from the 10 kg mass is
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{10}{3}\) m
(2). \(\displaystyle\frac{20}{3}\) m
(3). \(\displaystyle10\) m
(4). \(\displaystyle5\) m
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{10}{3}\) m
(2). \(\displaystyle\frac{20}{3}\) m
(3). \(\displaystyle10\) m
(4). \(\displaystyle5\) m
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The ratio of the radius of gyration of a thin uniform disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to its plane to the radius of gyration of the disc about its diameter is
(1). 2 : 1
(2). \(\sqrt{2}\) : 1
(3). 4 : 1
(4). 1 : \(\sqrt{2}\)
(1). 2 : 1
(2). \(\sqrt{2}\) : 1
(3). 4 : 1
(4). 1 : \(\sqrt{2}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A uniform rod of length 200 cm and mass 500 g is balanced on a wedge placed at 40 cm mark. A mass of 2 kg is suspended from the rod at 20 cm and another unknown mass 'm' is suspended from the rod at 160 cm mark as shown in the figure. Find the value of 'm' such that the rod is in equilibrium. (g = 10 m/s2)
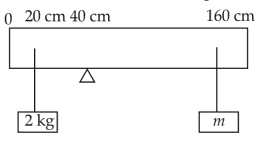
(1). 1 / 2 kg
(2). 1 / 3 kg
(3). 1 / 6 kg
(4). 1 / 12 kg

(1). 1 / 2 kg
(2). 1 / 3 kg
(3). 1 / 6 kg
(4). 1 / 12 kg
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Two particles of mass 5 kg and 10 kg respectively are attached to the two ends of a rigid rod of length 1 m with negligible mass.The centre of mass of the system from the 5 kg particle is nearly at a distance of
(1). 50 cm
(2). 67 cm
(3). 80 cm
(4). 33 cm
(1). 50 cm
(2). 67 cm
(3). 80 cm
(4). 33 cm
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Find the torque about the origin when a force of \(3\, \hat{j}\, \text{N}\) acts on a particle whose position vector is \(2\, \hat{k}\, m\).
(1). \(6\, \hat{j}\, \text{Nm}\)
(2). \(-6\, \hat{i}\, \text{Nm}\)
(3). \(6\, \hat{k}\, \text{Nm}\)
(4). \(6\, \hat{i}\, \text{Nm}\)
(1). \(6\, \hat{j}\, \text{Nm}\)
(2). \(-6\, \hat{i}\, \text{Nm}\)
(3). \(6\, \hat{k}\, \text{Nm}\)
(4). \(6\, \hat{i}\, \text{Nm}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A solid cylinder of mass 2 kg and radius 4 cm is rotating about its axis atthe rate of 3 rpm. The torque required to stop it after \(2\,\pi\) revolutions is
(1). \(2 \times 10^6\,N m\)
(2). \(2 \times 10^ {−6}\,N m\)
(3). \(2 \times 10^{ −3}\,N m\)
(4). \(12 \times 10^{ −4}\,N\)
(1). \(2 \times 10^6\,N m\)
(2). \(2 \times 10^ {−6}\,N m\)
(3). \(2 \times 10^{ −3}\,N m\)
(4). \(12 \times 10^{ −4}\,N\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A disc of radius 2 m and mass 100 kg rolls on a horizontal floor. Its centre of mass has speed of 20 cm ∕ s. How much work is needed to stop it?
(1). 1 J
(2). 3 J
(3). 30 kJ
(4). 2 J
(1). 1 J
(2). 3 J
(3). 30 kJ
(4). 2 J
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A solid sphere is in rolling motion. In rolling motion a body possesses translational kinetic energy (\(K_t\)) as well as rotational kinetic energy (\(K_r\)) simultaneously. The ratio \(K_t\,:\,\)(\( K_t\, +\, K_ r\)) for the sphere is
(1). 7:10
(2). 5:7
(3). 10:7
(4). 2:5
(1). 7:10
(2). 5:7
(3). 10:7
(4). 2:5
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A solid sphere is rotating freely about its symmetry axis in free space.The radius of the sphere is increased keeping its mass same. Which ofthe following physical quantities would remain constant for the sphere?
(1). Angular velocity
(2). moment of inertia
(3). Rotational kinetic energy
(4). Angular momentum
(1). Angular velocity
(2). moment of inertia
(3). Rotational kinetic energy
(4). Angular momentum
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Three objects, A (a solid sphere), B (a thin circular disk) and C (a circular ring), each have the same mass M and radius R. They all spin with the same angular speed ω about their own symmetry axes. The amounts of work (W) required to bring them to rest, would satisfy the relation
(1). \(\text{W}_ C\, >\, \text{W}_B\, >\, \text{W}_A \)
(2). \(\text{W}_A\, >\, \text{W}_B\, >\, \text{W}_C\)
(3). \(\text{W}_B\, >\, \text{ W}_ A\, >\, \text{W }_C\)
(4). \(\text{W}_A\, >\, \text{W}_C\, >\, \text{W}_B\)
(1). \(\text{W}_ C\, >\, \text{W}_B\, >\, \text{W}_A \)
(2). \(\text{W}_A\, >\, \text{W}_B\, >\, \text{W}_C\)
(3). \(\text{W}_B\, >\, \text{ W}_ A\, >\, \text{W }_C\)
(4). \(\text{W}_A\, >\, \text{W}_C\, >\, \text{W}_B\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The moment of the force, \(\vec{F} = 4\hat{i} + 5\hat{j} − 6\hat{k}\) at (2, 0, −3), about the point (2, −2, −2), is given by
(1). \(- 8\hat{i} − 4\hat{j} − 7\hat{k}\)
(2). \(−4\hat{i} −\hat{j} − 8\hat{k}\)
(3). \(−7\hat{i} − 8\hat{j} − 4\hat{k}\)
(4). \(−7\hat{i} − 4\hat{j} − 8\hat{k}\)
(1). \(- 8\hat{i} − 4\hat{j} − 7\hat{k}\)
(2). \(−4\hat{i} −\hat{j} − 8\hat{k}\)
(3). \(−7\hat{i} − 8\hat{j} − 4\hat{k}\)
(4). \(−7\hat{i} − 4\hat{j} − 8\hat{k}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
(1). \(0.25\, \text{rad}\, s^{−2}\)
(2). \(25\, \text{rad}\, s^{−2}\)
(3). \(5\, m\,s^{−2}\)
(4). \(25\, m\,s^{−2}\)
(1). \(0.25\, \text{rad}\, s^{−2}\)
(2). \(25\, \text{rad}\, s^{−2}\)
(3). \(5\, m\,s^{−2}\)
(4). \(25\, m\,s^{−2}\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Two discs of same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2.They are brought into contact face to face coinciding the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{4} I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(2). \(\displaystyle I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{8} I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} I \left(ω_1 + ω_2\right)^2\)
(1). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{4} I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(2). \(\displaystyle I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(3). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{8} I \left(ω_1 − ω_2\right)^2\)
(4). \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} I \left(ω_1 + ω_2\right)^2\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Which of the following statements are correct?
(1) Centre of mass of a body always coincides with the centre of gravity of the body.
(2) Centre of mass of a body is the point at which the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
(3) A couple on a body produces both transnational and rotational motion in a body.
(4) Mechanical advantage greater than one means that small effort can be used to lift a large load.
(1). (1) and (2)
(2). (2) and (3)
(3). (3) and (4)
(4). none of the above
(1) Centre of mass of a body always coincides with the centre of gravity of the body.
(2) Centre of mass of a body is the point at which the total gravitational torque on the body is zero.
(3) A couple on a body produces both transnational and rotational motion in a body.
(4) Mechanical advantage greater than one means that small effort can be used to lift a large load.
(1). (1) and (2)
(2). (2) and (3)
(3). (3) and (4)
(4). none of the above
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A disc and a sphere of same radius but different masses roll off on two inclined planes of the same altitude and length. Which one of the two objects gets to the bottom of the plane first?
(1). Both reach at the same time
(2). Depends on their masses
(3). Disk
(4). Sphere
(1). Both reach at the same time
(2). Depends on their masses
(3). Disk
(4). Sphere
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
A uniform circular disc of radius 50 cm at rest is free to turn about an axis which is perpendicular to its plane and passes through its centre. It is subjected to a torque which produces a constant angular acceleration of 2.0 rad s−2. Its net acceleration in s−2 at the end of 2.0 S is approximately
(1). 6.0
(2). 3.0
(3). 8.0
(4). 7.0
(1). 6.0
(2). 3.0
(3). 8.0
(4). 7.0
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
