Home >> My Performance >> My Topic Test Performance >> My Question Performance
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests !
Questions Available: 22
Questions Attempted: 10
Number of Attempts: 15
Correct Attempts: 8
Total Time Spent: 00:30
Avg Time Per Question: 00:02
My Question Performance Summary in Full Tests
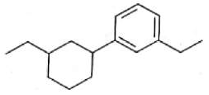
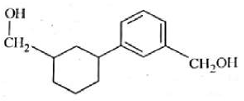
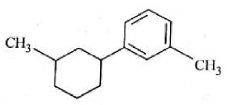
Identify product (A) in the following reaction:

(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).

(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
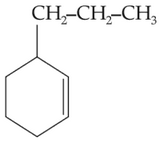
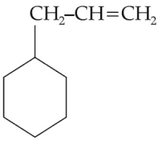
An alkene on ozonolysis gives methanal as one of
the product. Its structure is :
(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).
(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
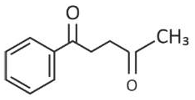
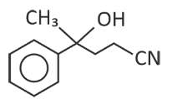
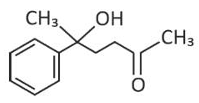
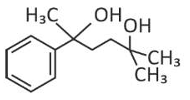
The major product of the following reaction is
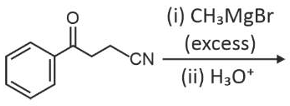
(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).

(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Identify the suitable reagent for the following conversion
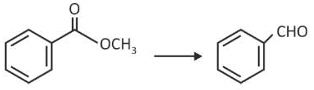
(1). \(H_2/Pd-BaSO_4\)
(2). (i) \(LiAIH_4\), (ii) \(H^+ /H_2O\)
(3). (i) \(AIH\left(iBu\right)_2\), (ii) \(H_2O\)
(4). (i) \(NaBH_4\), (ii) \(H^+ / H_2O\)

(1). \(H_2/Pd-BaSO_4\)
(2). (i) \(LiAIH_4\), (ii) \(H^+ /H_2O\)
(3). (i) \(AIH\left(iBu\right)_2\), (ii) \(H_2O\)
(4). (i) \(NaBH_4\), (ii) \(H^+ / H_2O\)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The correct order of decreasing acidity of the following aliphatic acids is :
(1). HCOOH > (СН3)3ССООН > (СН3)2СНСООH > СН3COOH
(2). (СНз)3ССООН > (СН3)2СHCOOH > СН3СООН > НСООН
(3). СН3СООН > (СН3)2СHСOOH > (СН3)3ССООН > HCOOH
(4). НСООН > СН3СООН > (СН3)2СНСООH > (СН3)3ССООН
(1). HCOOH > (СН3)3ССООН > (СН3)2СНСООH > СН3COOH
(2). (СНз)3ССООН > (СН3)2СHCOOH > СН3СООН > НСООН
(3). СН3СООН > (СН3)2СHСOOH > (СН3)3ССООН > HCOOH
(4). НСООН > СН3СООН > (СН3)2СНСООH > (СН3)3ССООН
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
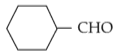
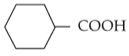
For the given reaction:
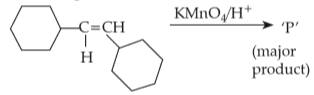
'P' is
(1).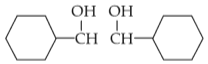
(2).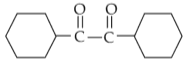
(3).
(4).

'P' is
(1).
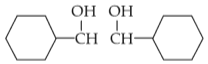
(2).
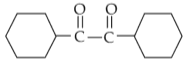
(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
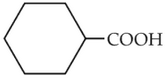
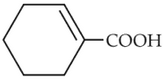
Complete the following reaction:

(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).

(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
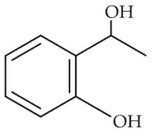
Identify the major product obtained in the
following reaction:
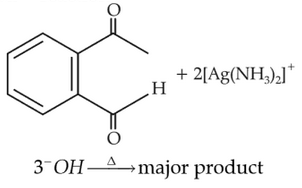
(1).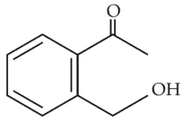
(2).
(3).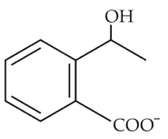
(4).

(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
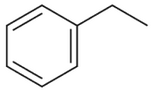
Identify the final product [D] obtained in the
following sequence of reactions.

(1).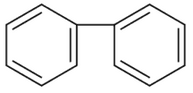
(2).
(3).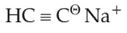
(4).

(1).

(2).

(3).
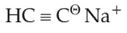
(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
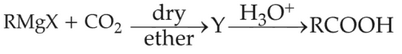
What is Y in the above reaction?
(1). RCOO-Mg+X
(2). R2CO-Mg+X
(3). RCOO-X+
(4). (RCOO)2Mg
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons ofcomparable molecular masses because of weakmolecular association in aldehydes and ketones dueto dipole - dipole interactions.
Statement II : The boiling points of aldehydesand ketones are lower than the alcohols of similarmolecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding.
In the light of the above statements, choose themost appropriate answer from the given below:
(1). Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(2). Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(3). Statement I is correct but Statement II isincorrect
(4). Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Statement I : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons ofcomparable molecular masses because of weakmolecular association in aldehydes and ketones dueto dipole - dipole interactions.
Statement II : The boiling points of aldehydesand ketones are lower than the alcohols of similarmolecular masses due to the absence of H-bonding.
In the light of the above statements, choose themost appropriate answer from the given below:
(1). Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(2). Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(3). Statement I is correct but Statement II isincorrect
(4). Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Match List-I with List-II.
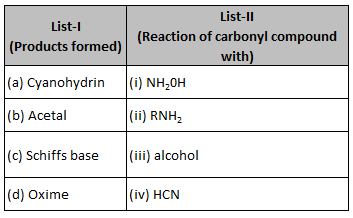
Choose the correct answer from the options givenbelow:
(1). (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(2). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(3). (a) - (i), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iv)
(4). (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)

Choose the correct answer from the options givenbelow:
(1). (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(2). (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(3). (a) - (i), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iv)
(4). (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
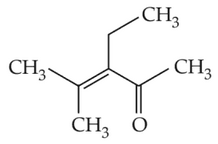
Which one of the following is not formed whenacetone reacts with 2-pentanone in the presenceof dilute NaOH followed by heating?
(1).
(2).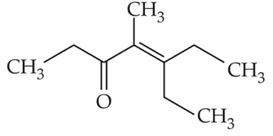
(3).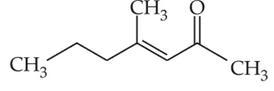
(4).
(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Reaction between benzaldehyde and acetophenone
in presence of dilute NaOH is known as:
(1). Cannizzaro's reaction
(2). Cross Cannizzaro's reaction
(3). Cross Aldol condensation
(4). Aldol condensation
(1). Cannizzaro's reaction
(2). Cross Cannizzaro's reaction
(3). Cross Aldol condensation
(4). Aldol condensation
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Reaction between acetone and methyl magnesium chloride followed by hydrolysis will give:
(1). Sec. butyl alcohol
(2). Tert. butyl alcohol
(3). Isobutyl alcohol
(4). Isopropyl alcohol
(1). Sec. butyl alcohol
(2). Tert. butyl alcohol
(3). Isobutyl alcohol
(4). Isopropyl alcohol
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
(1). formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
(2). more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction.
(3). formation of carboxylate ion.
(4). formation of intramolecular H-bonding.
(1). formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
(2). more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction.
(3). formation of carboxylate ion.
(4). formation of intramolecular H-bonding.
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
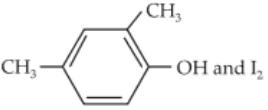
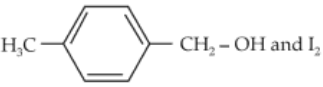
Compound A, C8H10O, is found to react with NaOI (produced by reacting Y with NaOH) and yields a yellow precipitate with characteristic smell.
A and Y are respectively :
(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).
A and Y are respectively :
(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
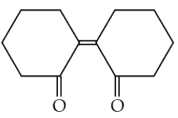
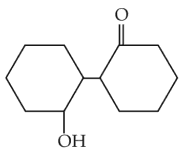
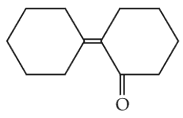
Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol condensation followed by heating ?
(1).
(2).
(3).
(4).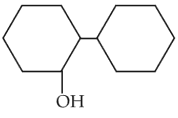
(1).

(2).

(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Consider the reaction
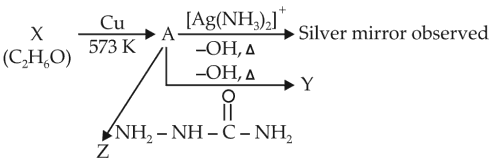
Identify A, X, Y, and Z
(1). A-Ethanol, X-Acetaldehyde, Y-Butanone, Z-Hydrazone
(2). A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanoic acid, Y-Acetate ion, Z-hydrazine
(3). A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanol, Y-Ethanoic acid, Z-Semicarbazide
(4). A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone

Identify A, X, Y, and Z
(1). A-Ethanol, X-Acetaldehyde, Y-Butanone, Z-Hydrazone
(2). A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanoic acid, Y-Acetate ion, Z-hydrazine
(3). A-Methoxymethane, X-Ethanol, Y-Ethanoic acid, Z-Semicarbazide
(4). A-Ethanal, X-Ethanol, Y-But-2-enal, Z-Semicarbazone
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
Identify A and predict the type of reaction
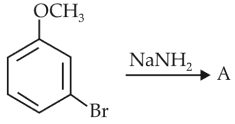
(1).
(2).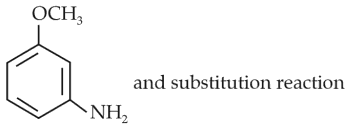
(3).
(4).

(1).

(2).
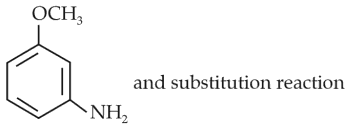
(3).

(4).

Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon, is
(1). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration
(2). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as carbonylation
(3). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
(4). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol
(1). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration
(2). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as carbonylation
(3). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
(4). a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
The product formed by the reaction of an aldehyde with a primary amine is
(1). ketone
(2). carboxylic acid
(3). aromatic acid
(4). schiff base
(1). ketone
(2). carboxylic acid
(3). aromatic acid
(4). schiff base
Number of Attempts: 2
Correct Attempts: 1
Time Taken: 00:04
Average Time: 00:02
