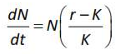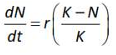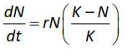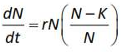Home >> Topics >> Organisms and Populations
Unattempted Questions
Questions Available: 23
Year: 2024
Topic: Organisms and Populations
1.
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: Gause’s competitive exclusion principle states that two closely related species competing for different resources cannot exist indefinitely.
Statement II: According to Gause’s principle, during competition, the inferior will be eliminated. This may be true if resources are limiting.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Statement I: Gause’s competitive exclusion principle states that two closely related species competing for different resources cannot exist indefinitely.
Statement II: According to Gause’s principle, during competition, the inferior will be eliminated. This may be true if resources are limiting.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Solution
Year: 2022
Topic: Organisms and Populations
2.
While explaining interspecific interaction of
population, (+) sign is assigned for beneficial
interaction, (-) sign is assigned for detrimental
interaction and (0) for neutral interaction. Which
of the following interactions can be assigned (+)
for one species and (-) for another species involved
in the interaction?