Home >> Topics >> Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Unattempted Questions
Questions Available: 21
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2023
Topic: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
6.
Given below are two statements: One is labelled
as Assertion A and the other is labelled as
Reason R:
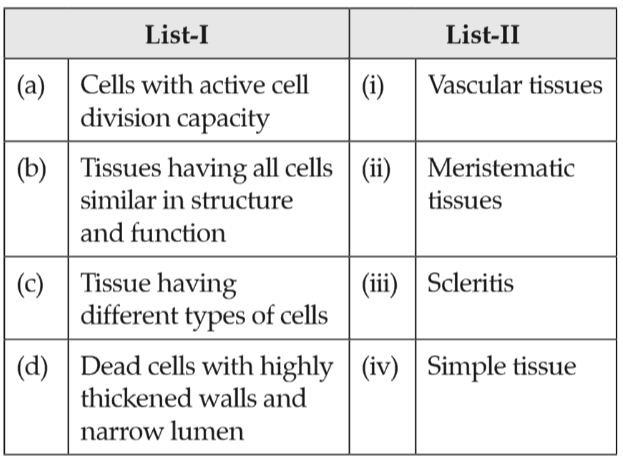
Assertion A : Late wood has fewer xylary elements with narrow vessels.
Reason R: Cambium is less active in winters.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Assertion A : Late wood has fewer xylary elements with narrow vessels.
Reason R: Cambium is less active in winters.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2020
Topic: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
12.
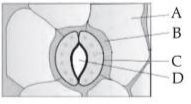
The transverse section of a plant shows following
anatomical features:
(a) Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(b) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(c) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(d) Phloem parenchyma absent.
ldentify the category of plant and its part:
(a) Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(b) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(c) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(d) Phloem parenchyma absent.
ldentify the category of plant and its part: