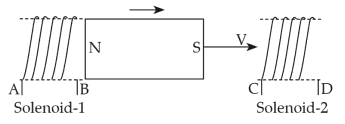
Home >> Topics >> Magnetism and matter
Unattempted Questions
Questions Available: 15
Solution
Year: 2024
Topic: Magnetism and matter
2.
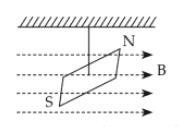
In a uniform magnetic field of 0.049T, a magnetic needle performs 20 complete oscillations in 5 seconds as shown. The moment of inertia of the needle is \(9.8×10^{−6} kgm^2\). If the magnitude of magnetic moment of the needle is \(x×10^{−5} Am^2\), then the value of 'x ' is :

Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2024
Topic: Magnetism and matter
5.
A sheet is placed on a horizontal surface in front of a strong magneticpole. A force is needed to:
A. hold the sheet there if it is magnetic.
B. hold the sheet there if it is non-magnetic.
C. move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if it is conducting.
D. move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if it is both,non-conducting and non-polar.
Choose the correct statement(s) from the options given below:
A. hold the sheet there if it is magnetic.
B. hold the sheet there if it is non-magnetic.
C. move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if it is conducting.
D. move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if it is both,non-conducting and non-polar.
Choose the correct statement(s) from the options given below:
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2021
Topic: Magnetism and matter
9.
A uniform conducting wire of length \(12\,a\) and resistance 'R' is wound up as a current carrying coil in the shape of,
(i) an equilateral triangle of side 'a'.
(ii) a square of side 'a'.
The magnetic dipole moments of the coil in each case respectively are
(i) an equilateral triangle of side 'a'.
(ii) a square of side 'a'.
The magnetic dipole moments of the coil in each case respectively are
Solution
Solution
Solution
Year: 2018
Topic: Magnetism and matter
12.
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from